DNA finder
This command is used to find vertically aligned DNA molecules in images. Typically these are 20-50 kb DNAs that are surface immobilized and fluorescently stained. After locating the ends of the DNA molecules, this command can also perform 2D Gaussian fitting to determine the location of each end with subpixel accuracy. There are a lot of possible input/output options to allow for customizability so the same tool can be used with multiple image and DNA types.
Input
- Image - The active image selected will be used by the DNA Finder. The name of this image will be displayed below the image stack in the dialog.
- Region - Apply the tool to either the ‘whole image’, an ‘ROI from image’ or ‘ROIs from manager’.
- Channel - Select which channel to analyze in case a video with multiple channels is provided as input.
Find
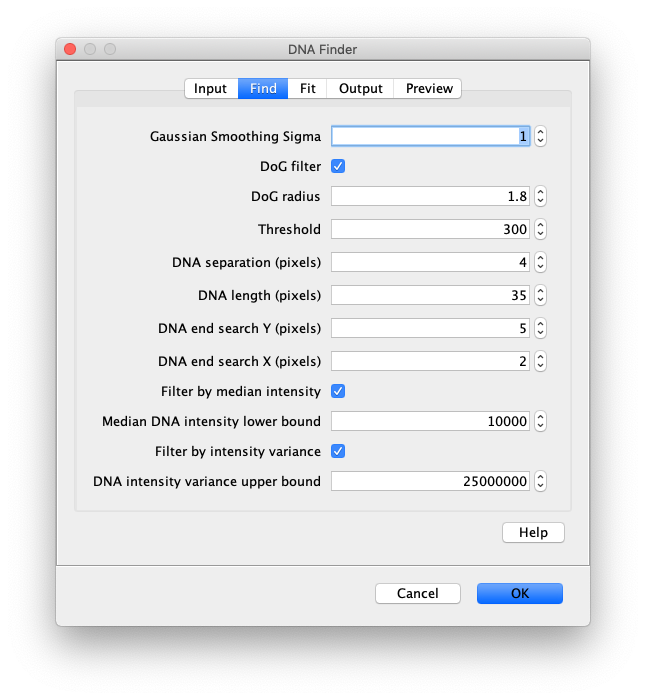
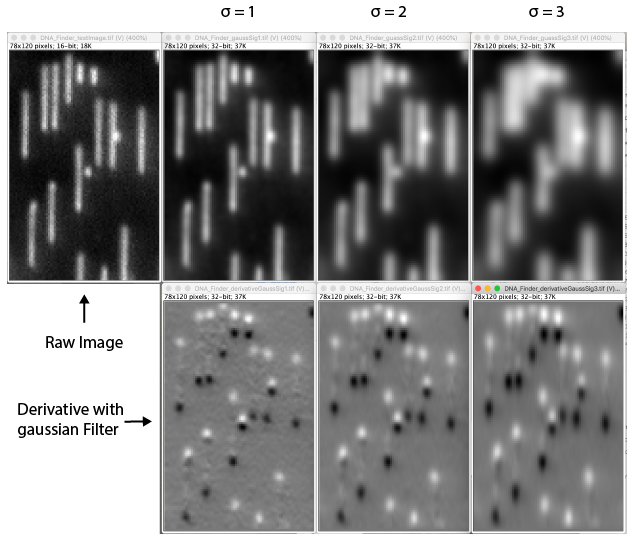
- Gaussian Smoothing Sigma - The sigma used for gaussian smoothing. The DNA Finder uses the scijava OpService op derivativeGauss which filters the image with a combined gaussian smoothing and takes the derivative. Usually a sigma of 1 is usually sufficient. Higher sigma values might lead to too much smoothing and obscure important features.
- DoG filter - If checked the image will be processed with a Difference of Gaussian (DoG) filter before peak finding. Using an appropriately chosen radius this filter enhances real peaks with signal spread among several pixels and suppresses salt and pepper noise as demonstrated in this systematic study. If unchecked the raw image will be used for peak finding.
- DoG radius - The radius used for DoG filtering. The value chosen should reflect the size of the desired peaks. Decimal numbers are permitted.

- Threshold - This is threshold in pixel value used for peak detection. Pixels with values above this threshold are considered peaks and pixels below this threshold are considered background. For everyday peak detection, the DoG filter should be used in which case this threshold using on the DoG filtered image. In this case, we have found that values between 40 and 60 provide optimal detection for typical single-molecule observations. If the DoG Filter is turned off this threshold reflects raw pixel values in the input image.
- DNA separation (in pixels) - This is the minimum allowed distance between peaks (edges here), This means only the pixel with the highest (or lowest) intensity within this radius will be accepted as a peak, even if there are other peaks above the threshold within this radius region. This is an important setting since most peaks have nearby pixels that are also above the detection threshold, but we only want to detect each peak once. If you see a lot of overlapping DNAs increasing this setting will help.
- DNA length (in pixels) - The mean length in pixels of the DNA you want to find. This value is used when attempting to link positive peaks to their negative counterparts to find DNAs.
- DNA end search y (in pixels) - The y radius used during the DNA end search. Larger values will ensure DNAs of different lengths are found.
- DNA end search x (in pixels) - The x radius used during the DNA end search. If the DNAs are vertically aligned this value should be kept low. As this value is increase cross linking between adjacent DNAs might occur.
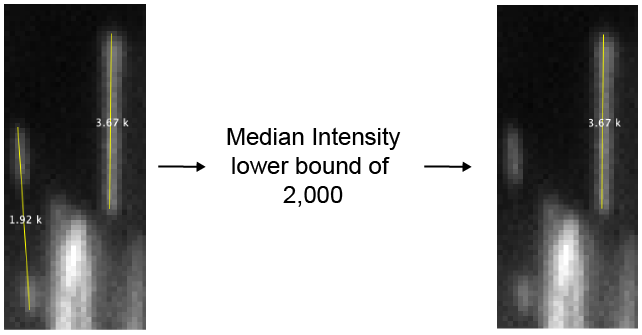
- Filter by median intensity - If checked DNAs will be removed if their median intensity is below the “Median DNA intensity lower bound” value.
- Median DNA intensity lower bound - A lower bound threshold for the median intensity of the DNA molecule. Sometimes two small DNA fragments are considered a single DNA. In this case the median DNA intensity is low. This filter can be used to remove these.
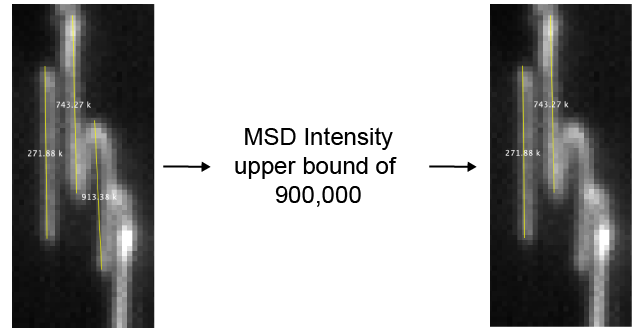
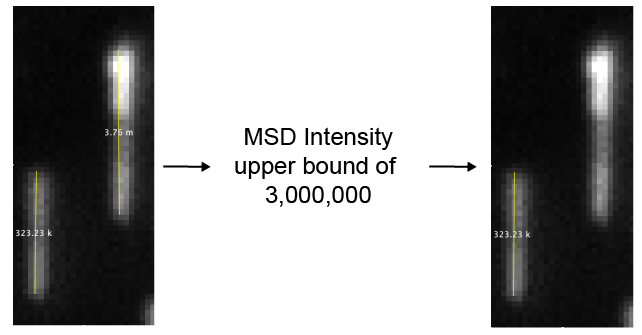
- Filter by intensity variance - If checked DNAs will be removed if the variance of their intensity is above the “DNA intensity variance upper bound” value.
- DNA intensity variance upper bound - An upper bound threshold for the variance of the DNA intensity. Sometimes multiple DNAs clump together or form arches. These structures are sometimes detected as single DNA molecules, but have a large mean squared intensity deviation. Setting an upper bound threshold for the variance will remove these.
Fit
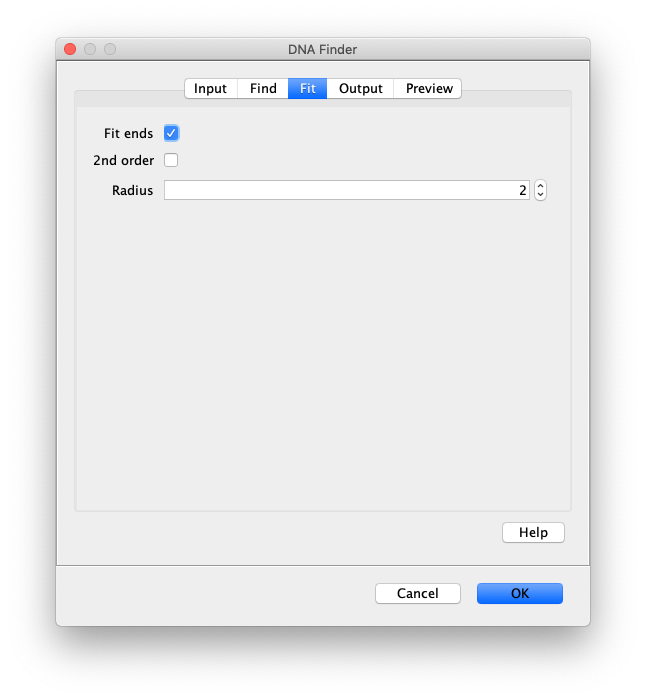
- Fit ends - If checked the DNA ends will be fit with 2D Gaussians to determine their sub pixel position. If left unchecked, all the remaining settings will be ignored and the peaks will be reported with their integer pixel positions. See the [[Peak Finder]] for further information about fitting.
- 2nd order - Will perform the subpixel fitting on the second derivative image. If turned off the first derivative image is used. The second derivative image will result in more accurate length estimate but may be less stable.
- Radius - The radius of pixels used for fitting. 0 is one pixel, 1 is 9 pixels, 2 is 25 pixels. Usually 2 is a pretty good estimate depending on the peak size. There needs to be some pixels at the edges close to background for an ideal fit.
Output
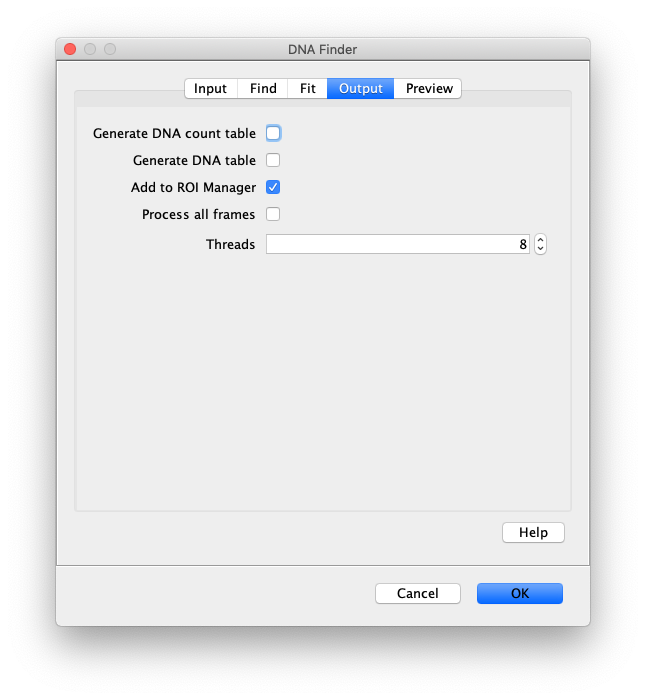
- Generate DNA count table - If checked a table will appear in which each row has the number of detected peaks for each slice.
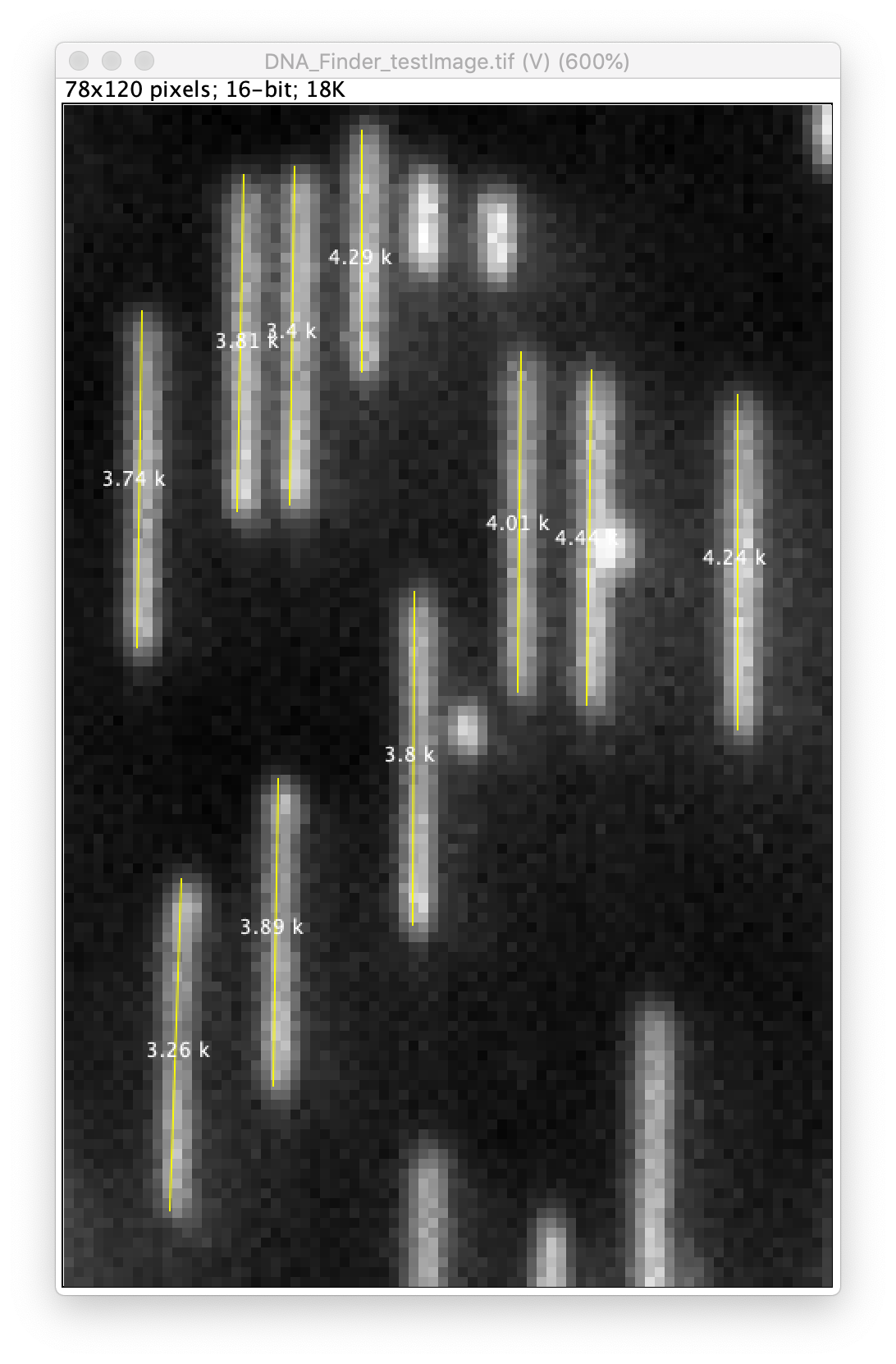
- Generate DNA table - If checked a table will be generated listing the positions of all detected peaks. x1, y1 for the top edges and x2, y2 for the bottom edges. Also, the length calculated from the coordinates as well as the median intensity and mean squared deviation of the intensity.
- Add to RoiManager - If checked, lines peaks will be added to the RoiManager. By default there will be UID names.
- Process all Frames - If checked the command will run on all frames in the video. For tables the T for each DNA is given in a separate column. For the RoiManager the position is set based on the T.
- Thread count - Determines how much computing power of your computer will be devoted to this calculation. A higher thread count decreases computing time.
Preview
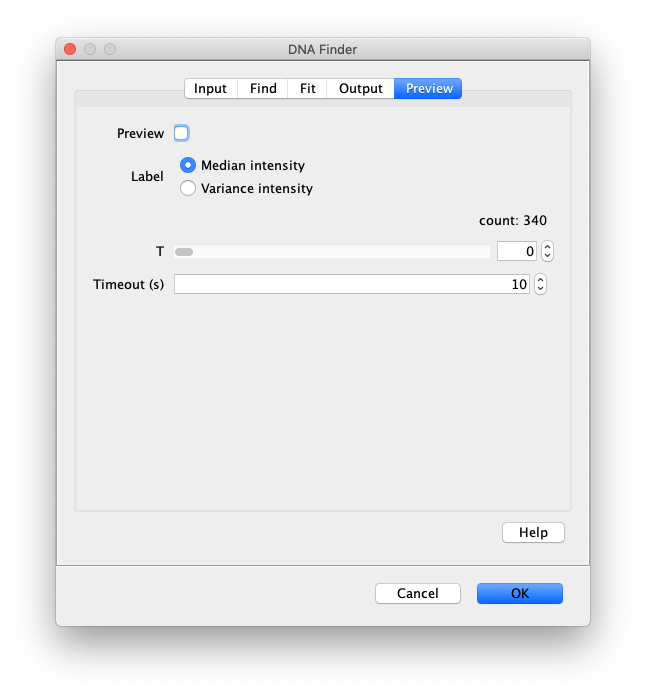
- Preview - Check this box to turn on preview mode. This will display an overlay of the DNAs that were located on the image. Sometime if you have a very large image this might be really slow, be patient. Otherwise, just make an ROI for preview testing, which will run faster. Once you have found the right settings you can cancel, remove the ROI, and run the command on the whole image with the correct settings.
- Label - Select between labeling the identified DNA molecules with the ‘Median intensity’ or ‘Variance intensity’ value.
- T - Select the frame to be displayed in the preview.
- Preview timeout(s) - Maximum computing time allowed to calculate the preview of the settings. If the video is too large or the settings are way off the computing time could become rather significant causing a crash of the system. Setting this limit prevents that.
Result
Several different kinds of results are possible depending on the settings used.
- Generate DNA count table - If checked a table will appear in which each row has the number of detected peaks for each slice.
- Generate DNA table - If checked a table will be generated listing the positions of all detected peaks. x1, y1 for the top edges and x2, y2 for the bottom edges. Also, the length calculated from the coordinates as well as the median intensity and mean squared deviation of the intensity.
- Add to RoiManager - If checked, lines peaks will be added to the RoiManager. By default there will be UID names.
- Process all Frames - If checked the command will run on all frames in the video. For tables the T for each DNA is given in a separate column. For the RoiManager the position is set based on the T.
How to run this Command from a groovy script
#@ Dataset dataset
#@ ImageJ ij
#@OUTPUT MarsTable dnaTable
import de.mpg.biochem.mars.table.*
import de.mpg.biochem.mars.image.*
import de.mpg.biochem.mars.image.command.*
//Make an instance of the Command you want to run...
DNAFinderCommand dnaFinder = new DNAFinderCommand();
//Populates @Parameters Services etc.. using the current context
//which we get from the ImageJ input...
dnaFinder.setContext(ij.getContext())
dnaFinder.setDataset(dataset)
dnaFinder.setUseROI(false)
dnaFinder.setGaussianSigma(1)
dnaFinder.setUseDogFilter(True)
dnaFinder.setDogFilterRadius(1.8)
dnaFinder.setThreshold(2)
dnaFinder.setMinimumDistance(4)
dnaFinder.setOptimalDNALength(34)
dnaFinder.setYDNAEndSearchRadius(27)
dnaFinder.setXDNAEndSearchRadius(3)
dnaFinder.setFilterByMedianIntensity(true)
dnaFinder.setMedianIntensityLowerBound(3000)
dnaFinder.setFilterByVariance(true)
dnaFinder.setVarianceUpperBound(900000)
dnaFinder.setFit(True)
dnaFinder.setFitSecondOrder(False)
dnaFinder.setFitRadius(2)
dnaFinder.setT(0)
dnaFinder.setGenerateDNACountTable(false)
dnaFinder.setGenerateDNATable(true)
dnaFinder.setAddToRoiManager(false)
dnaFinder.setProcessAllFrames(false)
//Run the Command
dnaFinder.run();
//Retrieve output from the command
dnaTable = dnaFinder.getDNATable()
//MarsTable dnaCountTable = dnaFinder.getDNACountTable()
//The other possible output is adding the peaks to the RoiManager
//in which case the RoiManager can then be use for further steps.
//However, keep in mind the RoiManager will probably not work
//in headless mode.