Gradient Calculator
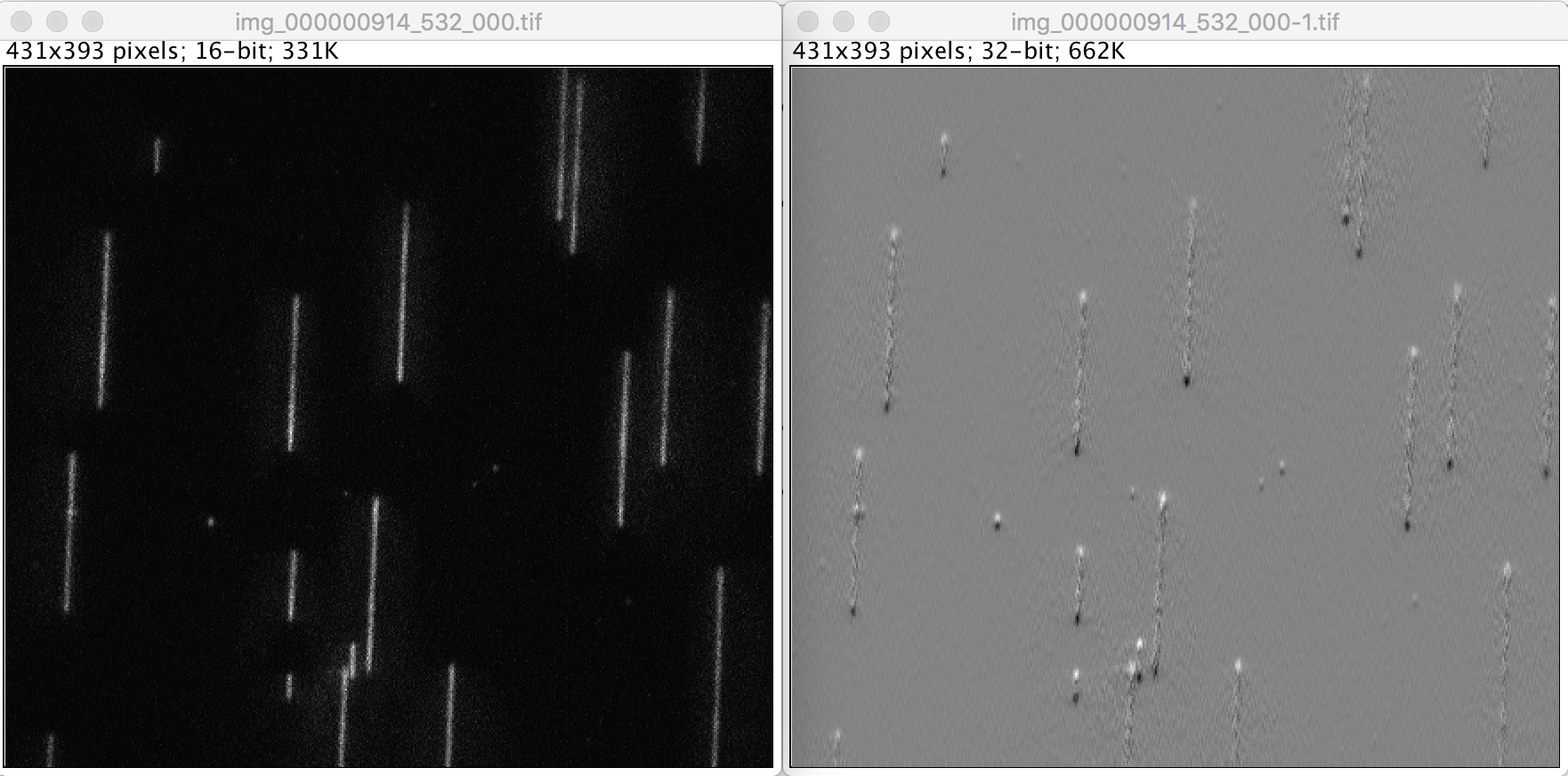
This command calculates the gradient (slope) of consecutive pixels in the y direction from top to bottom or from left to right. This is very useful for detecting the edges of stained DNA molecules. If the DNA molecules are aligned with the y-axis then the gradient image will have a positive peak at the top and negative peak at the bottom. Usually images cannot have negative values since pixels always have positive values, but in this case the output is a float image, so this is allowed.
At the boundaries, a reflected mirror image is used to calculate the slope. Sometimes this can cause edge effects, but not normally.
Inputs
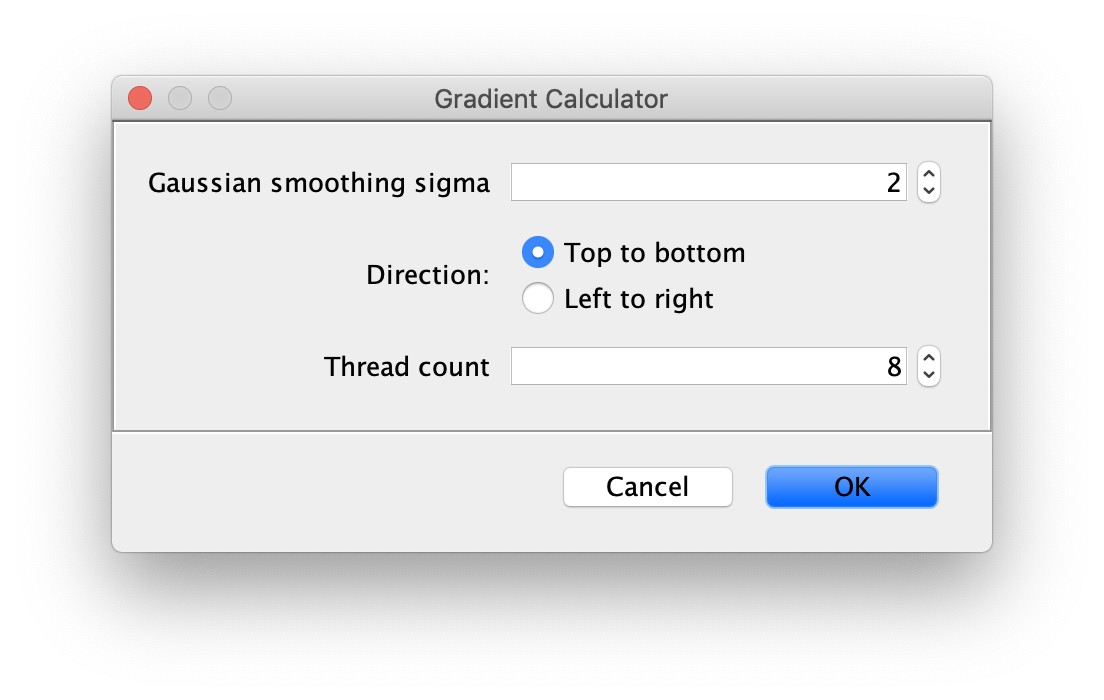
- Image - An image or sequence of images to calculate the gradient for. This doesn’t show up in the dialog since the active image is taken, but this is a required input.
- Gaussian smoothing sigma -
- Direction - Set in which direction the gradient should be calculated: top to bottom or left to right.
- Thread count - Determines how much computing power of your computer will be devoted to this calculation. A higher thread count decreases computing time.
Output
- Image - A sequence of gradient tif images. You can then open these as a new virtual stack and continue processing. Usually the next step is to use the PeakFinder and/or PeakTracker to find and track the DNA edges. The locations found by these tools should overlay perfectly with the original image prior to running the gradient tool. Meaning the slope is place at the same pixel position where it was calculated.
How to run this Command from a groovy script
#@ ImagePlus image
#@ ImageJ ij
import de.mpg.biochem.mars.ImageProcessing.*
//Make an instance of the Command you want to run...
final GradientCommand gradientCalculator = new GradientCommand();
//Populates @Parameters Services etc.. using the current context
//which we get from the ImageJ input...
gradientCalculator.setContext(ij.getContext())
gradientCalculator.setDataset(dataset)
gradientCalculator.setGaussianSigma(2)
gradientCalculator.setDirection("Top to bottom")
//Run the Command